Food Manufacturing
-
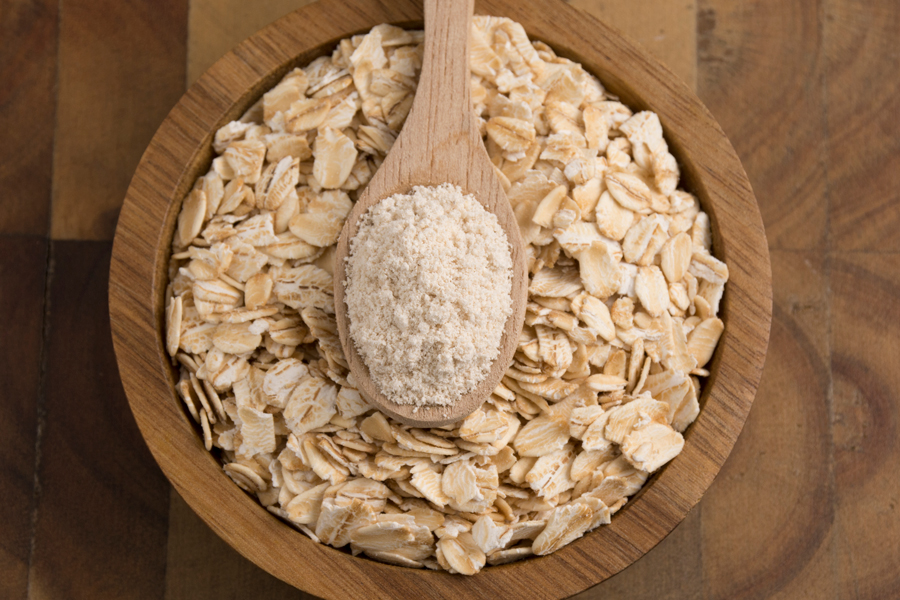

Oat okara, the nutritious byproduct of oat milk processing, is rich in protein and dietary fiber. Current practices often discard okara or use it as animal feed. Produced in large quantities, it represents not only a sustainability challenge but also a significant economic opportunity. With potential applications in food fortification and as a cost-effective ingredient in baked goods, snacks, and more, utilizing oat okara can reduce waste and add value to the production chain. Unlocking its potential benefits both the environment and the food industry.
Hualu Zhou and Anthony Stevanus Suryamiharja
|
-

An acidified food is a low-acid food to which acids (such as vinegar, lemon juice, citric acid, etc.) or acid foods (such as fruits or tomatoes) have been added to bring the equilibrium pH of the food to 4.6 or less, with equilibrium water activity greater than 0.85.
Kaitlyn Casulli
|
-

Using Hot-Fill-Hold: A Thermal Preservation Process. Processors of acidified foods are required to comply with federal, state, and local regulations (when applicable) for thermal processing to ensure the safety and shelf-stability of their products. The hot-fill-hold (HFH) process is a thermal processing technique used to inactivate pathogens and extend the shelf life of acidified products. Heating before filling allows for commercial sterilization of the product, and then filling the container with the hot product will sterilize the clean container.
Kaitlyn Casulli
|
-

When processing acidified foods, the hot-fill-hold process involves heating the product to around 180–200 °F, then filling, inverting, and holding for 2–5 minutes to achieve commercial sterility. Higher temperatures will generally correlate with shorter hold times, and lower temperatures will generally correlate with longer hold times.
Kaitlyn Casulli
|
-
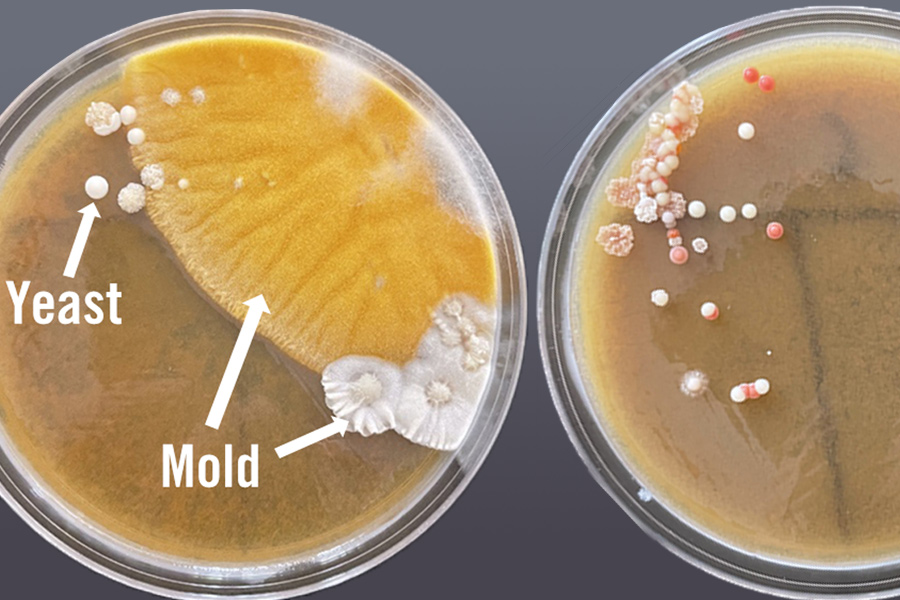
Wild yeast fermentations are an emerging trend in brewing that can provide a unique sensory experience for the consumer compared to beers brewed with commercial yeast strains. Wild yeast allows brewers to put a local story behind their beers by using strains isolated from the nearby environment. While wild yeasts can impart fruity, spicy, or sour flavors in beers without the addition of adjuncts, the beer’s sensory properties, yeast attenuation, and yeast’s alcohol tolerance are unpredictable, and evaluations must be conducted to determine the flavor profiles in beers brewed with wild yeast.
Kaitlyn Casulli
|
-
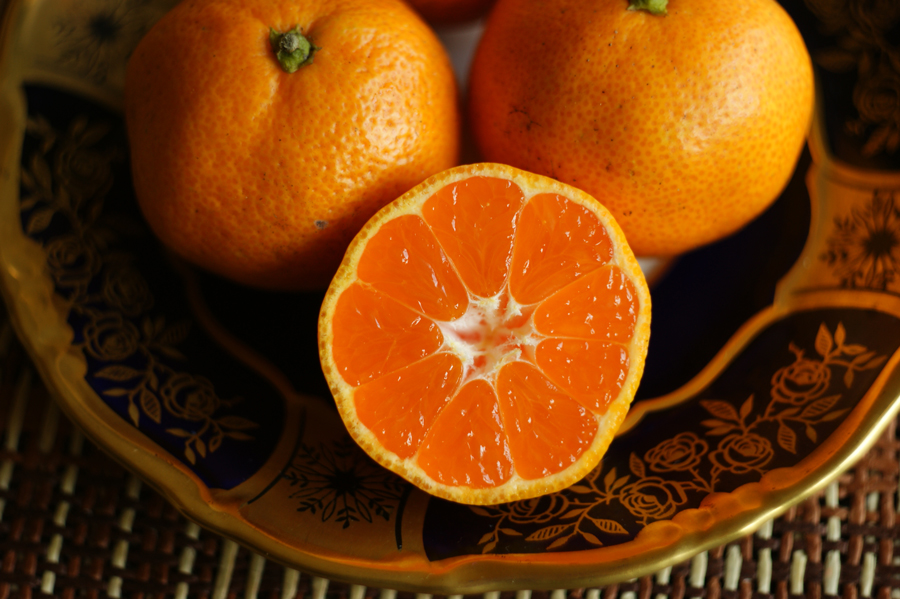

Additional author: Emma Moore, Department of Food Science & Technology. Satsuma oranges are a fast-growing commodity in Georgia. Satsumas are natural and excellent sources of sugars, organic acids, soluble fibers, vitamins, minerals, phytochemicals, and essential oils. Because of their nutritional content, satsuma oranges are considered functional foods (foods that provide health benefits and essential nutrition). Novel products may be produced from satsuma oranges and satsuma peels, including food ingredients such as soluble fibers and essential oils that may be appealing to health-conscious consumers interested in including more plant-based ingredients into their diets.
Fresh satsuma oranges have a short shelf-life. This publication describes the nutrients found in satsuma oranges and opportunities to develop high-value food ingredients from satsuma oranges. This information is timely and may help the local citrus industry diversify its current product portfolio. It also describes essential food safety concepts that may improve the overall competitiveness of the Georgia citrus industry.
Laurel Dunn and Kevin Mis Solval
|
-

U.S. poultry processors must meet regulatory requirements for Salmonella and Camplylobacter prevalence in all of the poultry products that they produce. Monitoring the efficacy of antimicrobial interventions (biomapping) during processing assists in meeting performance standards and improving microbiological quality of the products through better process control.
Harshavardhan Thippareddi and Manpreet Singh
|
-

Poultry processors have incorporated numerous antimicrobial interventions in the slaughter process to reduce the prevalence and/or concentrations of foodborne pathogens Salmonella and Campylobacter. The conventional process is to evaluate the efficacy of the incorporated antimicrobial interventions in reducing either indicator microorganisms or the foodborne pathogens immediately after the intervention step. This publication provides information on the two distinct elements of validation.
Harshavardhan Thippareddi and Manpreet Singh
|
-

“‘Clean label’ foods” generally refers to food products that are simple, natural, and minimally processed. Clean labeling is a food industry movement that caters to the consumer who wants food products to be as “real” and preservative-free as possible. Although “clean labeling” is becoming more ubiquitous among food companies, there is no formal definition for the term. It originates from consumer perception of “natural” foods and is then self-defined by food companies, restaurants, and retailers.
In order to build a trustworthy relationship with consumers, more companies have removed or are planning to remove artificial ingredients from their products. However, this process is not easy, and manufacturers must ensure the efficacy, safety, quality, and cost-effectiveness of natural substitutes before using these alternatives widely.
Koushik Adhikari
|