Fruit and Vegetable Production Resources
-
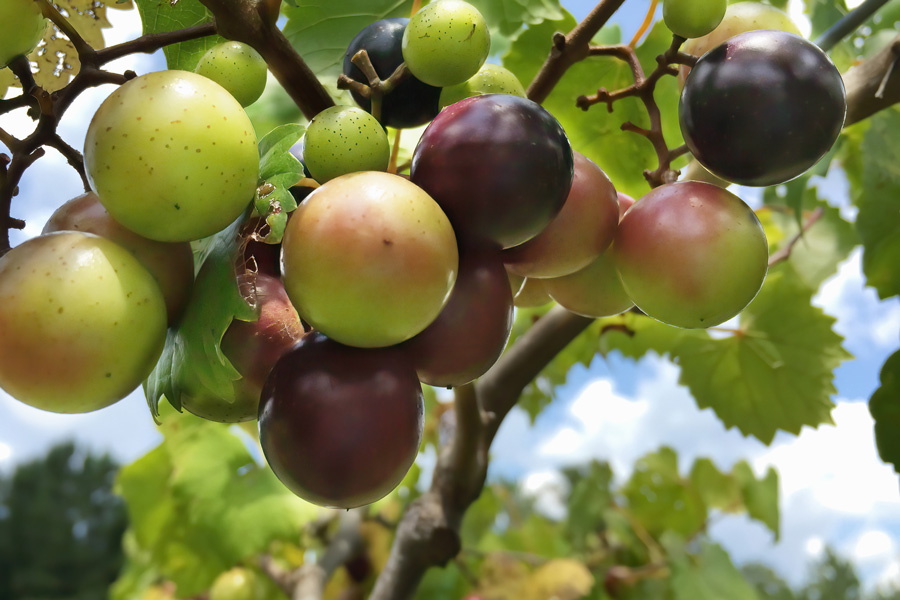

This 2023 update to the regional integrated pest management guide provides recommendations for muscadine grape production in the Southeastern U.S. Recommendations are based on information from the manufacturer’s label and performance data from research and Extension field tests. This publication is intended for use only as a guide. Specific rates and application methods are on the pesticide label, and these are subject to change at any time.
Phillip M. Brannen
|
-
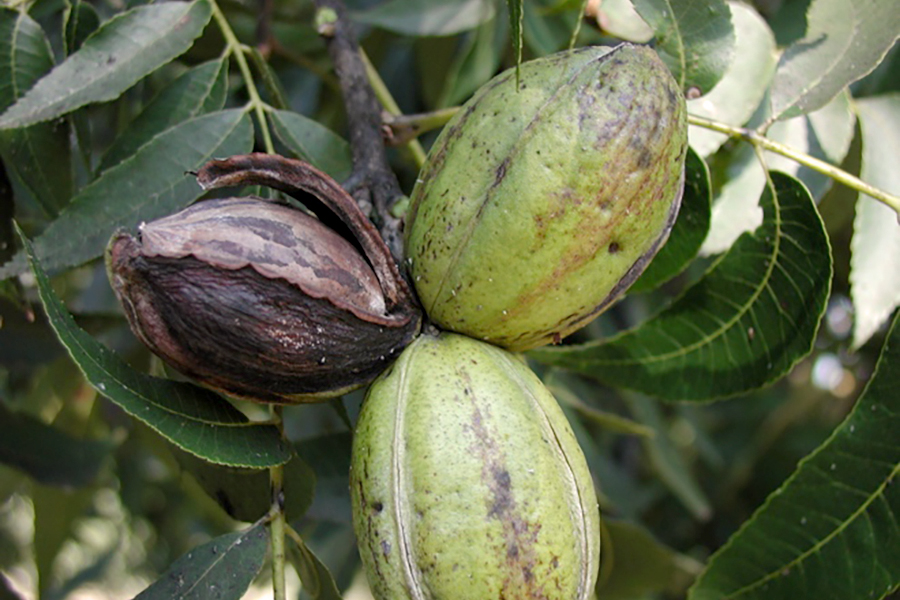

Some of the more difficult-to-diagnose pecan disorders include nutritional imbalances, nutrient deficiencies, or environmentally induced disorders. Some nutrients may be more available than others on certain soil types and under certain soil conditions, and complex interactions often occur between nutrients. This resource explains to pecan growers what to look for and how to handle these issues.
Lenny Wells
|
-
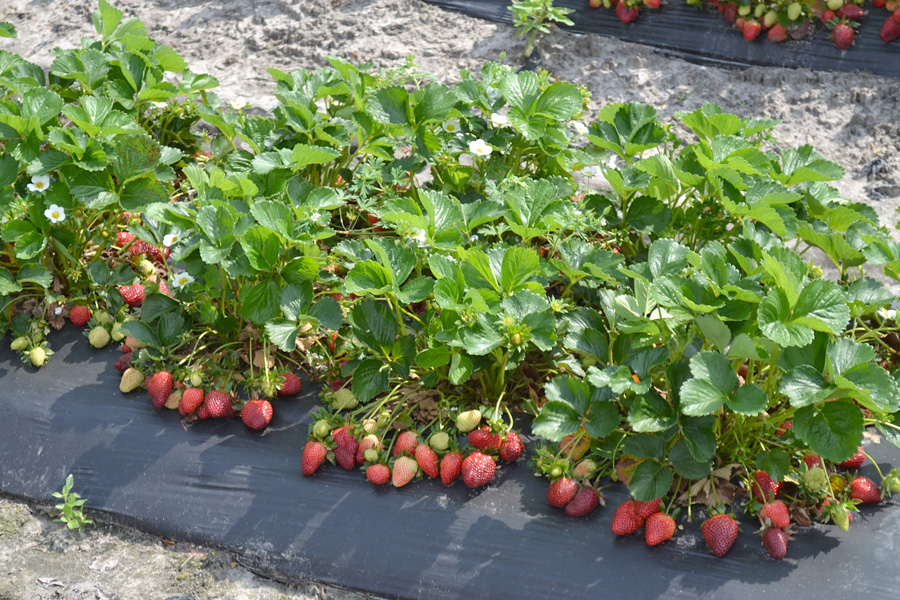

The 2023 edition of this regional integrated pest management guide provides recommendations for strawberry plasticulture production in the Southeastern U.S. Recommendations are based on information from the manufacturer’s label and performance data from research and Extension field tests. This publication is intended for use only as a guide. Specific rates and application methods are on the pesticide label, and these are subject to change at any time.
Phillip M. Brannen
|
-
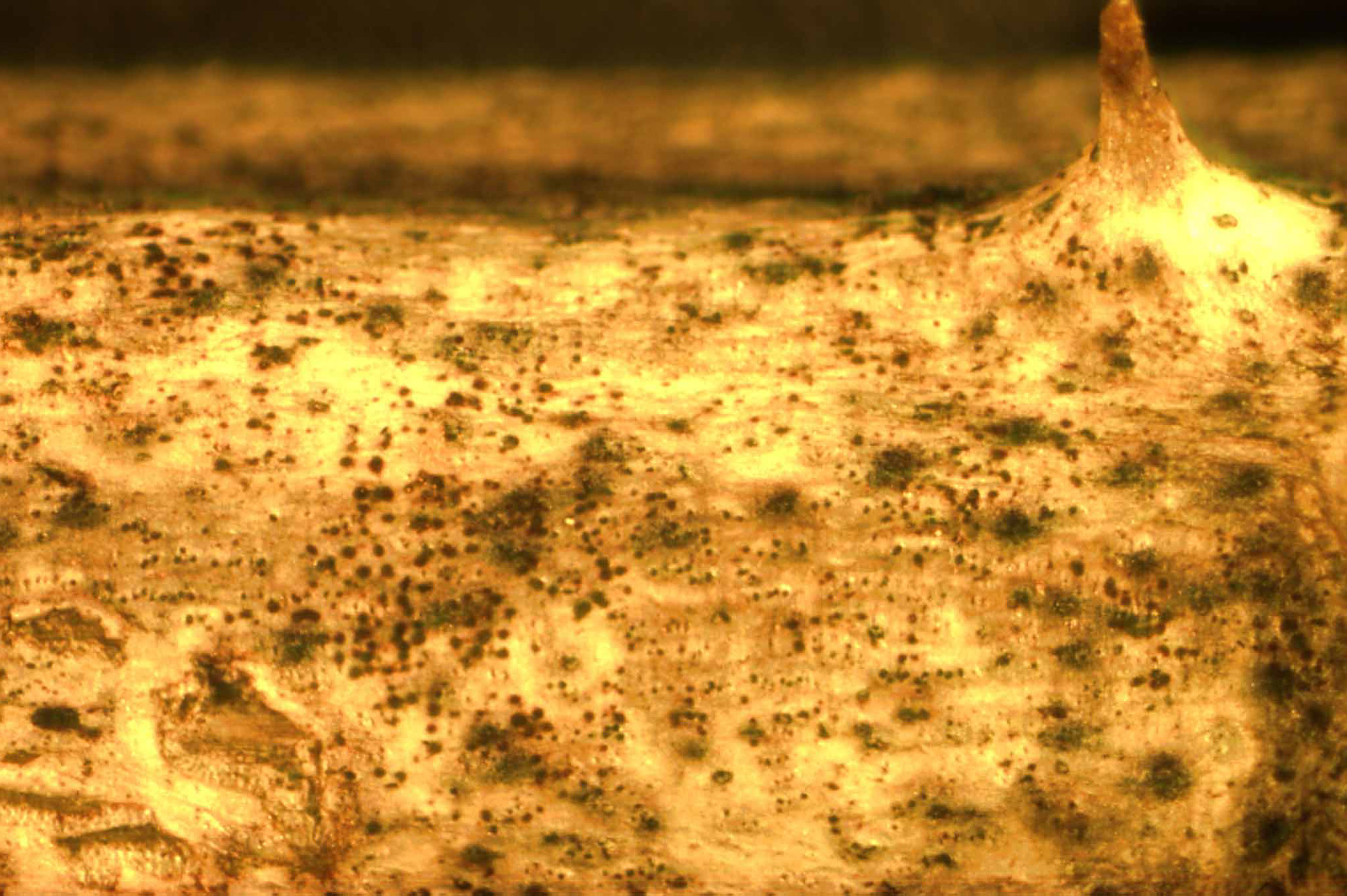
Cane blight can be a major disease of blackberry in the Southeast, resulting in severe losses. The wet, humid conditions observed in Georgia and other southeastern states allow for significant losses following pruning or other injuries to the primocane.
Phillip M. Brannen and Gerard W. Krewer
|
-
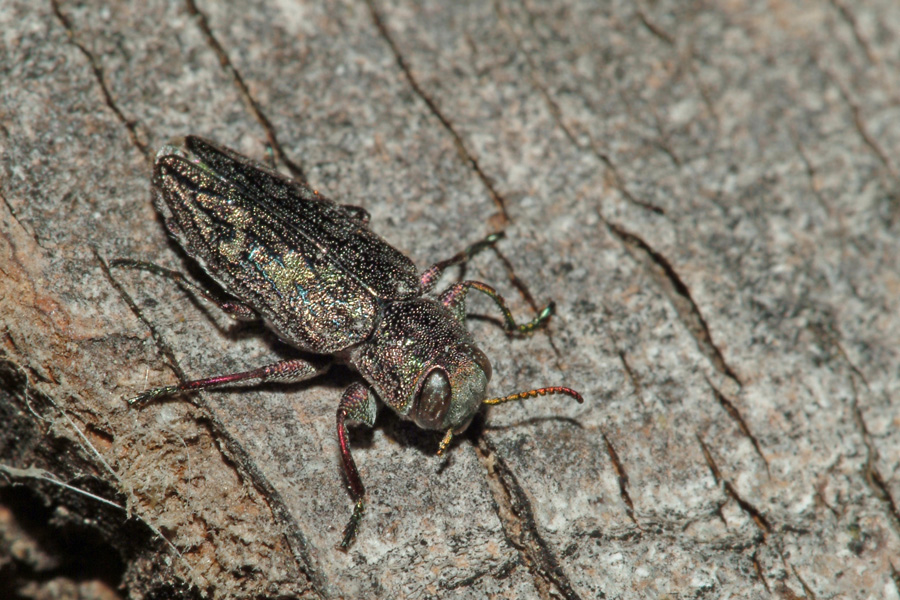

The flatheaded appletree borer is a polyphagous pest—so called because it feeds on multiple tree species—native throughout North America. Flatheaded appletree borers impact specialty crops such as fruit, nut, and ornamental trees. Nursery growers in Georgia face mild to moderate levels of infestation depending on the local beetle population size and favorable environmental conditions. Adult flatheaded appletree borers are metallic greenish-bronze and appear fattened in cross-section, which causes them to produce “D” or oval-shaped exit holes as they emerge from wood; these exit holes commonly are associated with buprestid beetles. The elytra or wing covers of flatheaded appletree borer adults have markings that appear as light-colored zigzagging bands. Larvae are cream-colored and have an enlarged, fattened thoracic segment behind the darker true head of the insect—this is what gives them the flatheaded name.
William G. Hudson, Shimat V. Joseph, and Zia Valerie Williamson
|
-
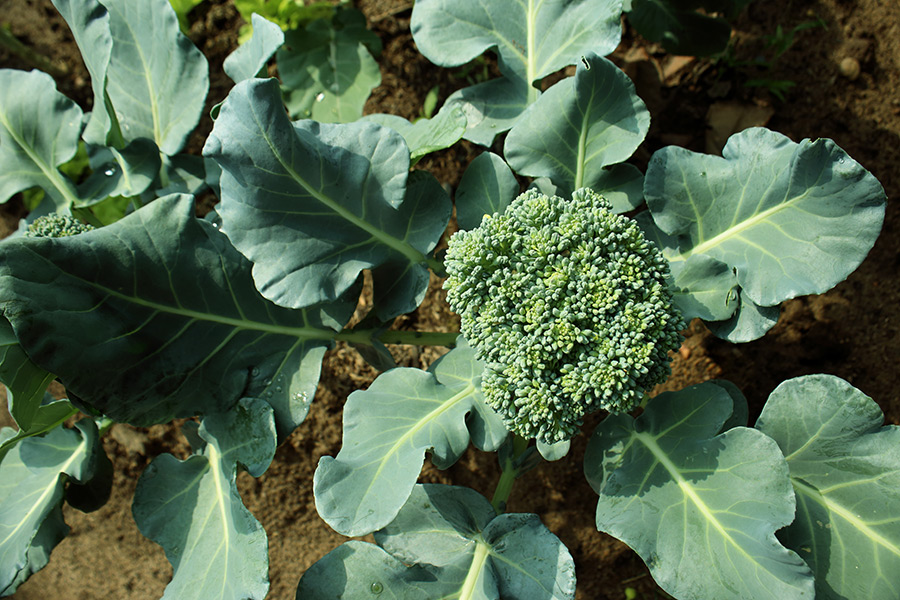

C 1258
Fall Vegetable Gardening
This publication covers fall vegetable production including planting dates, spacing, general culture of cool-season vegetables planted in Georgia in the fall. Many people consider the end of summer to be the end of gardening season. However, there is a whole other world of vegetables that can be planted in the fall garden in Georgia. Temperatures are milder, and there generally are fewer insects and diseases to contend with when planting in the fall. Cool-season vegetables are ironically planted in the late-summer heat, but thrive as they mature during cooler temperatures as the season progresses. Whether you choose to plant only a cover crop or to try your hand at some cool-season vegetables, planting for the fall growing season will keep your garden productive all year long.
Bob Westerfield
|
-
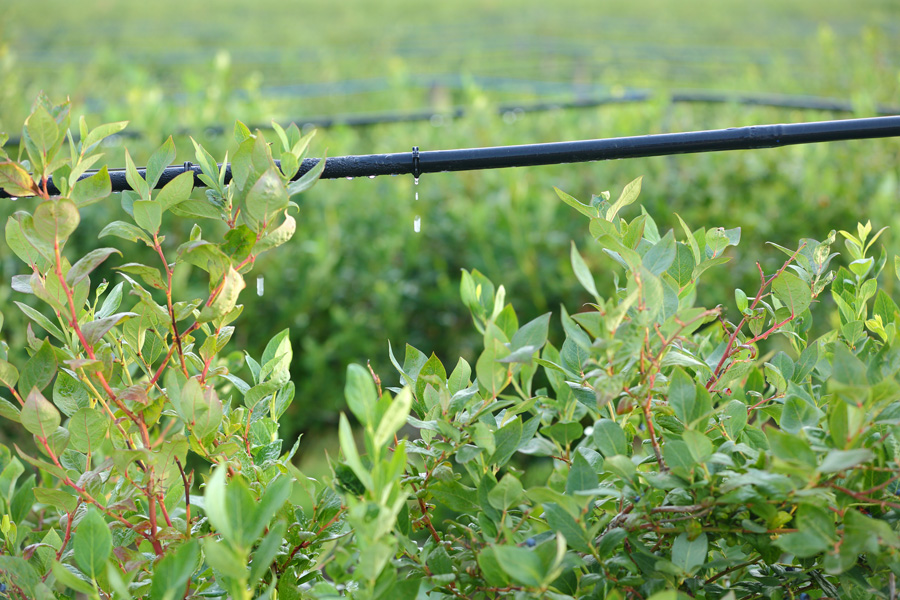

This circular is a review of water quality standards, calculations, and recommendations for water that will be used for irrigation of blueberries.
Gary L. Hawkins, Uttam K. Saha, Wesley Porter, Zilfina Rubio Ames, and Glendon H. Harris
|
-
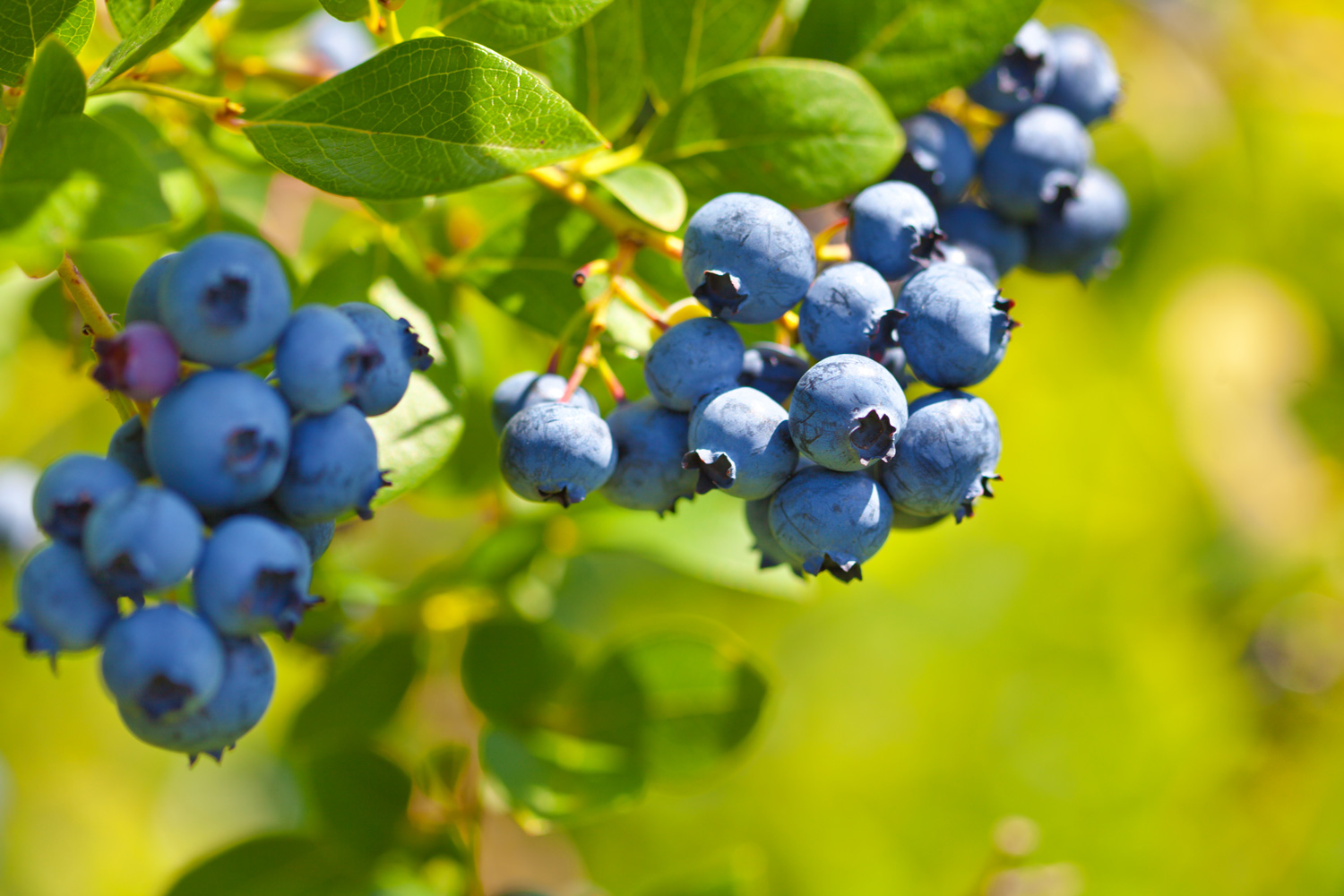

The 2023 edition of this publication covers integrated pest management information for blueberry producers in the Southeastern U.S. Recommendations are based on information from the manufacturer’s label and performance data from research and Extension field tests. This publication is intended for use only as a guide. Specific rates and application methods are on the pesticide label, and these are subject to change at any time.
Phillip M. Brannen and Ashfaq A. Sial
|
-

The commercial citrus industry in Georgia has only recently been established, with most groves planted after 2014. Initially,
satsuma mandarins (Citrus unshiu) on trifoliate rootstocks (Poncirus
trifoliata) were planted for their cold-hardiness, seedlessness, and
ease of peeling. Satsuma fruits begin to attain commercial maturity in
early November and usually avoid hard freezes in southern Georgia. As of
2022, approximately 75% of the 3,300 acres of citrus planted in Georgia are
satsumas, but that proportion is trending downward. To strengthen the new
Georgia citrus industry, growers recently have begun to diversify their citrus
varieties. Little is known about how these varieties will perform under Georgia
weather and soil conditions. Therefore, research is necessary to determine what
varieties can best tolerate Georgia’s winter weather and to determine cultural
norms such as maturation time, fruit quality, and insect and disease tolerance. This publication is associated with Annual Publication 127, the annual publication containing each season’s harvest data.Jake Price
|