Well Water
-

C 858-8
Hydrogen Sulfide and Sulfate
This publication describes hydrogen sulfide and sulfate and its effects on household water quality.
David E. Kissel Ph.D, Pamela R. Turner, Uttam K. Saha, Jake Mowrer, and Leticia S Sonon
|
-

C 858-7
Coliform Bacteria in Your Water
This publication contains information about identifying and controlling coliform bacteria in household water.
David E. Kissel Ph.D, Pamela R. Turner, Uttam K. Saha, and Leticia S Sonon
|
-

Shock chlorination is the process by which home water systems such as wells, springs, and cisterns are disinfected using household liquid bleach (or chlorine). Shock chlorination is the most widely recommended means of treating bacterial contamination in home water systems. This publication contains guidelines for safely and effectively using shock chlorination — a standard treatment for sanitizing your well system.
Uttam K. Saha, Pamela R. Turner, David E. Kissel Ph.D, and Leticia S Sonon
|
-

C 858-3
Home Water Quality and Treatment
The quality of your water supply can have both an immediate and a prolonged effect on the health of your household. Many Americans, especially those dependent upon well water, assume that their water is safe and healthy. Unfortunately, this is not always the case. This publication contains basic information about home water quality and treatment.
David E. Kissel Ph.D, Pamela R. Turner, Uttam K. Saha, and Leticia S Sonon
|
-
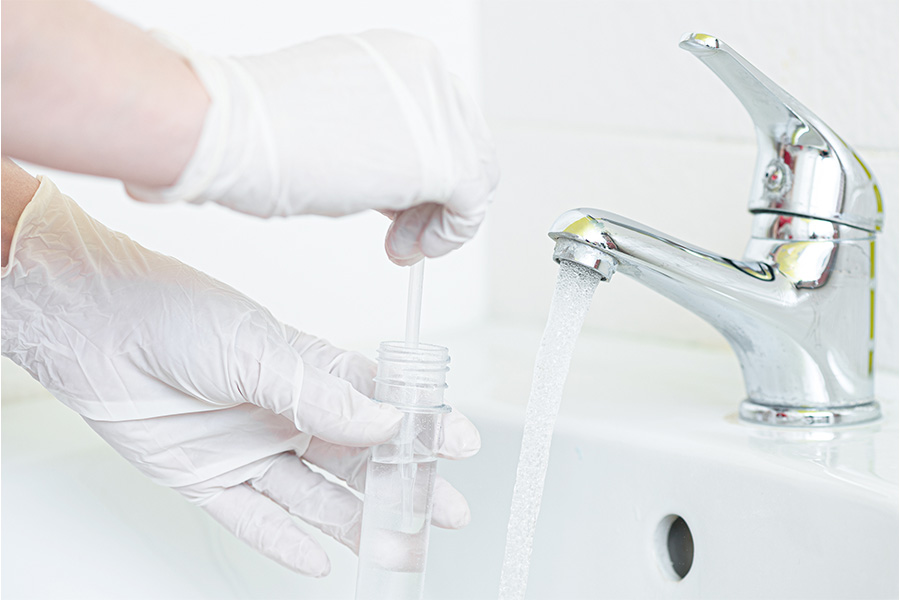
C 858-2
Testing for Water Quality
The quality and safety of drinking water is of great concern to many Americans today because of an increased interest in health and environmental quality. This new focus on water quality has led many Americans to consider testing their water. This publication is intended to help you understand water testing and to identify the tests needed.
David E. Kissel Ph.D, Pamela R. Turner, Uttam K. Saha, Jake Mowrer, and Leticia S Sonon
|
-
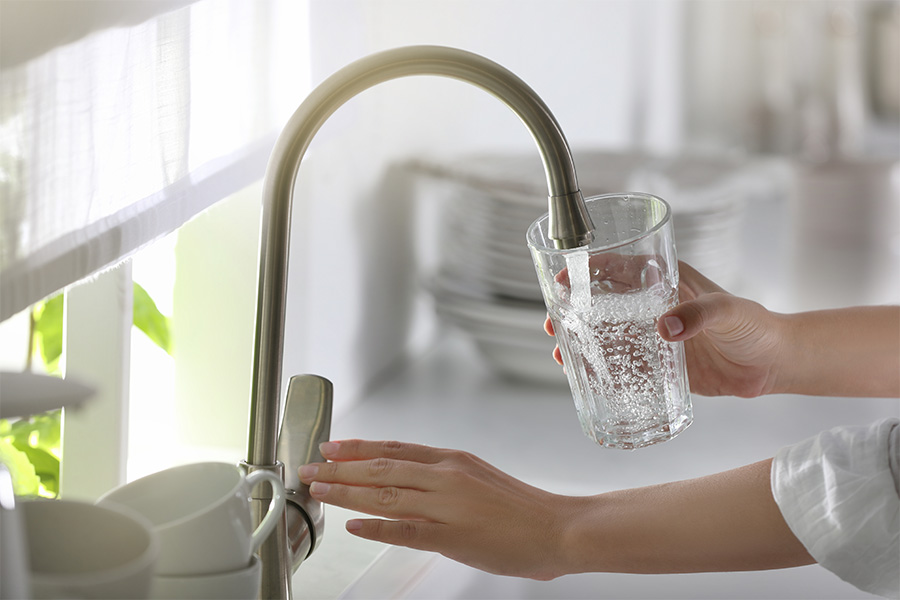

This publication explains how to identify and remove hydrogen sulfide and sulfate from household water.
David E. Kissel Ph.D, Pamela R. Turner, Uttam K. Saha, Jake Mowrer, and Leticia S Sonon
|
-

If you are one of the many Americans who use groundwater for drinking,
the proper protection of your well and wellhead is essential for the health of your family, yourself and your neighbors. This publication contains information about protecting your well and wellhead from contaminants.David E. Kissel Ph.D, Pamela R. Turner, Uttam K. Saha, and Leticia S Sonon
|
-

C 858-12
Arsenic in Your Water
Arsenic in your drinking water poses a threat to your health. Since private systems are more susceptible to arsenic than public water systems, private well owners should take steps to guard their health. Measures include routine water supply testing and wellhead maintenance and protection.
David E. Kissel Ph.D, Uttam K. Saha, and Leticia S Sonon
|
-

C 1027-11
Sources of Water for the Garden
This publication discusses the advantages and disadvantages of various sources of water for a community or school garden, including municipal water, rivers or creeks, ponds, wells and rainwater.
Bob Westerfield and David Berle
|