An additional author is Candace Tucker, MS, NDTR.
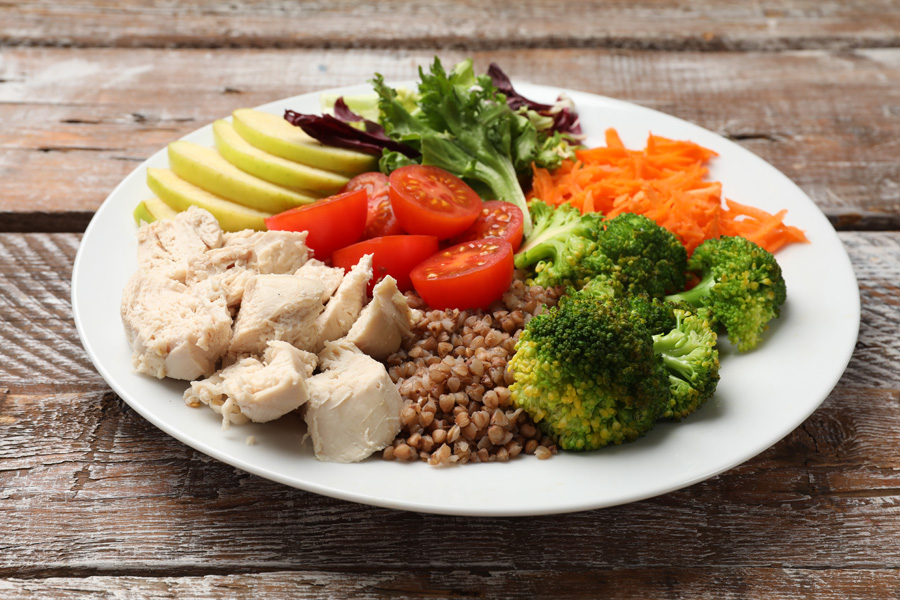
The Diabetes Plate Method is an approach to creating a healthy eating pattern. It may be used alone or in combination with other tools to create a healthy eating pattern and meet your nutrition and health goals. Research has shown that the Diabetes Plate Method can help people with diabetes lower their A1c (improve blood glucose management).
It is a simple visual approach that can be tailored to cultural preferences and tastes. This method suggests filling ½ of your plate with non-starchy vegetables. Fill ¼ of the plate with carbohydrate foods like beans, peas, rice, or starchy vegetables. Fill the remaining ¼ of the plate with lean protein foods like chicken, fish, lean meat, or tofu. While not a precise method for carbohydrate counting, the Diabetes Plate Method should result in a meal that is moderate in the amount of carbohydrates.
Choose water or a low-calorie drink, like unsweetened tea, sparkling water, or other beverage without added sugar. Water is the best choice because it contains no carbohydrates to raise your blood glucose.
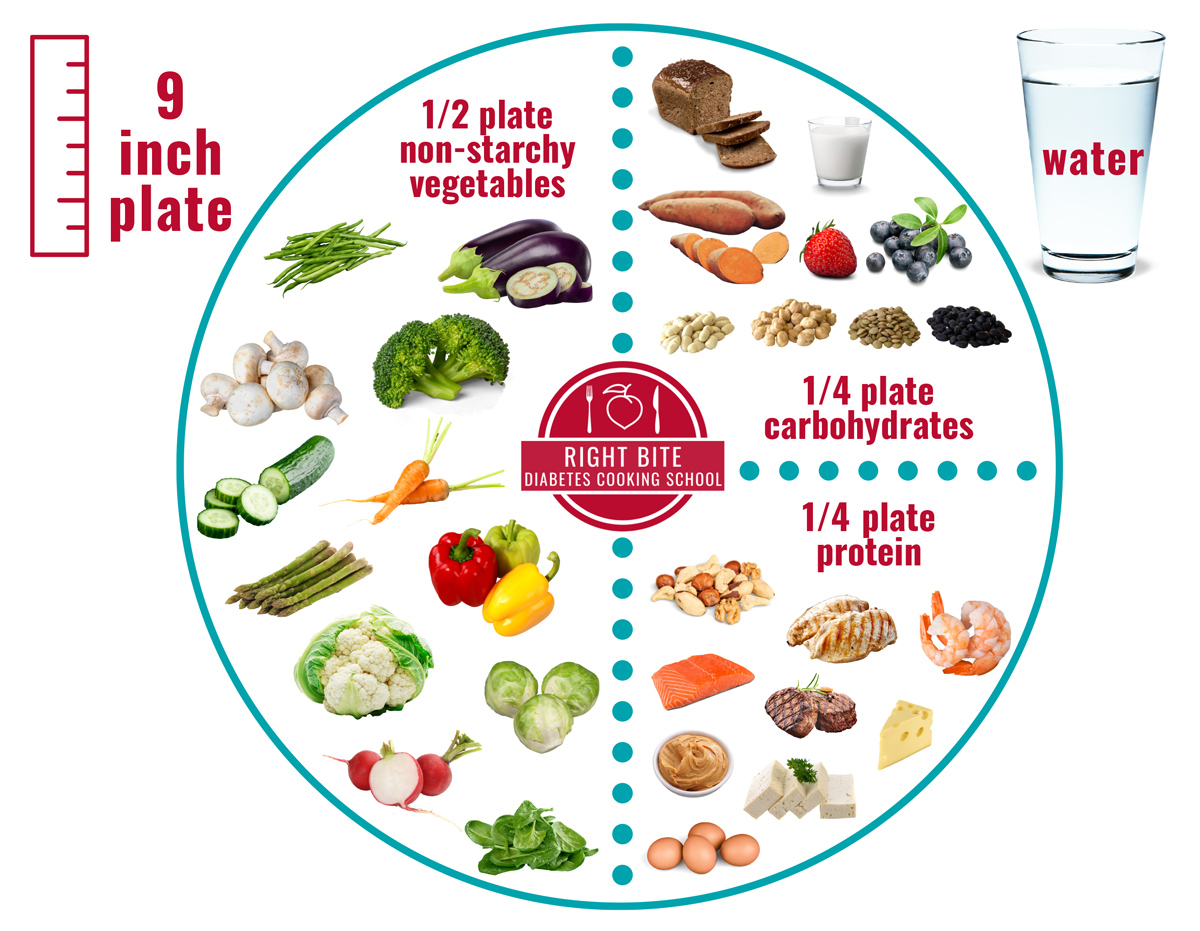
Choose a variety of carbohydrate foods for your meals and snacks, including dairy foods that are important for bone health. General carbohydrate recommendations per meal are 45–60 grams for women and 60–75 grams for men. Carbohydrate needs are different for everyone and depend on many factors, including age, sex, health conditions, and activity level. See your physician or registered dietitian for individualized carbohydrate recommendations.
References
American Diabetes Association. (2025). What is the diabetes plate? https://www.diabetesfoodhub.org/articles/what-is-the-diabetes-plate-method.html
American Diabetes Association Professional Practice Committee. (2024). Facilitating positive health behaviors and well-being to improve health outcomes: Standards of care in diabetes. Diabetes Care, 47(Supplement_1), S77–S110. https://doi.org/10.2337/dc24-S005









