Entomology Resources
-

This biennial publication contains the proceedings of the turfgrass field day carried out at the UGA Griffin campus every other year. The guide provides professionals with continuous, real-time access to the latest up-to-date information about turfgrass research studies, products, and turfgrass Extension activities, programs, and outreach. Topics will include, but are not limited to: crop and soil science, agronomy, weed science, plant pathology, entomology, economics, tissue culture, urban agriculture, irrigation, and student posters.
Clint Waltz, David Jespersen, and Bochra Amina Bahri
|
-
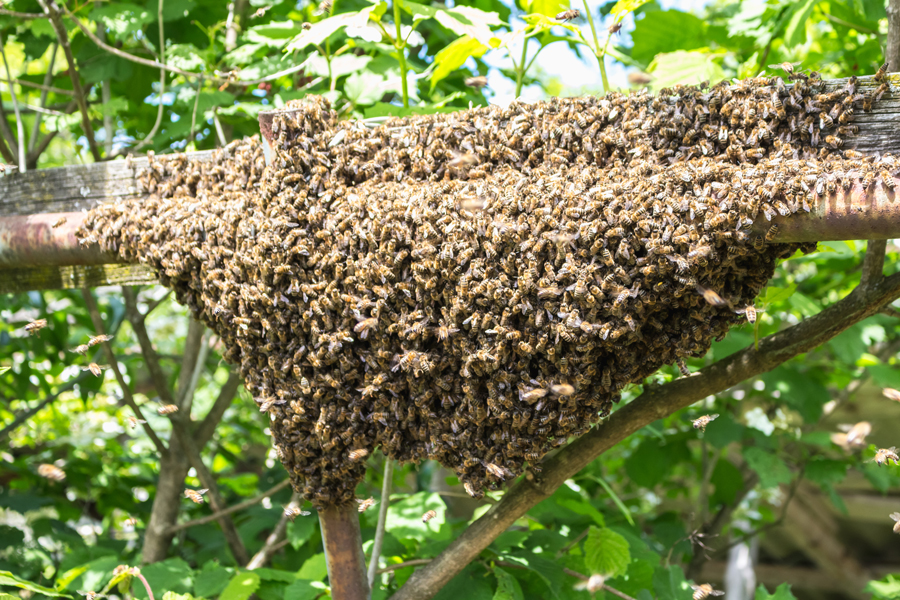

This circular is for property owners who have unwanted honey bee swarms on their lands or colonies nesting inside walls. It explains these natural processes and gives options for dealing with them.
Keith S Delaplane
|
-
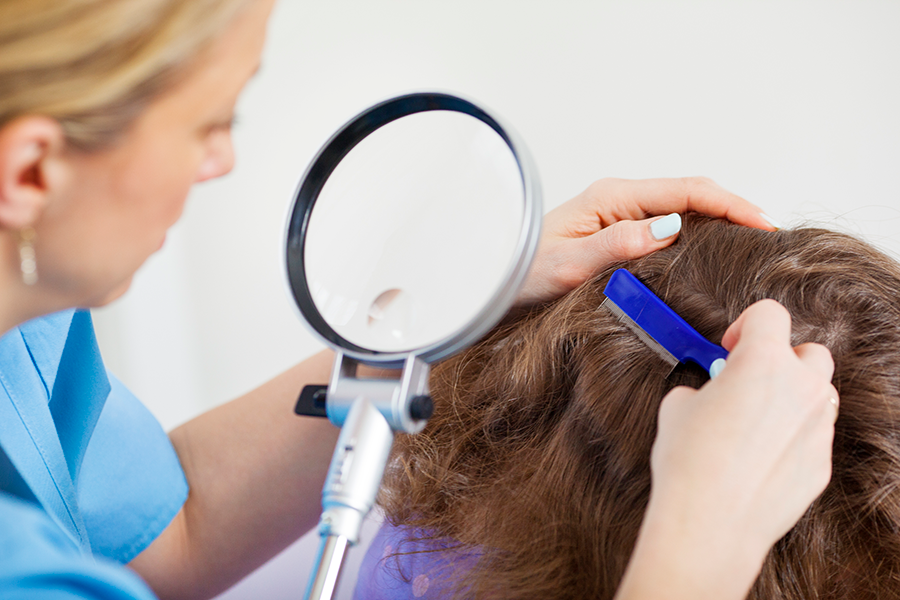
This guide discusses how to prevent and treat head lice outbreaks in schools.
Allison Faye Johnson
|
-

This guide for parents explains what to do — and what not to do — when a child gets head lice.
Allison Faye Johnson
|
-
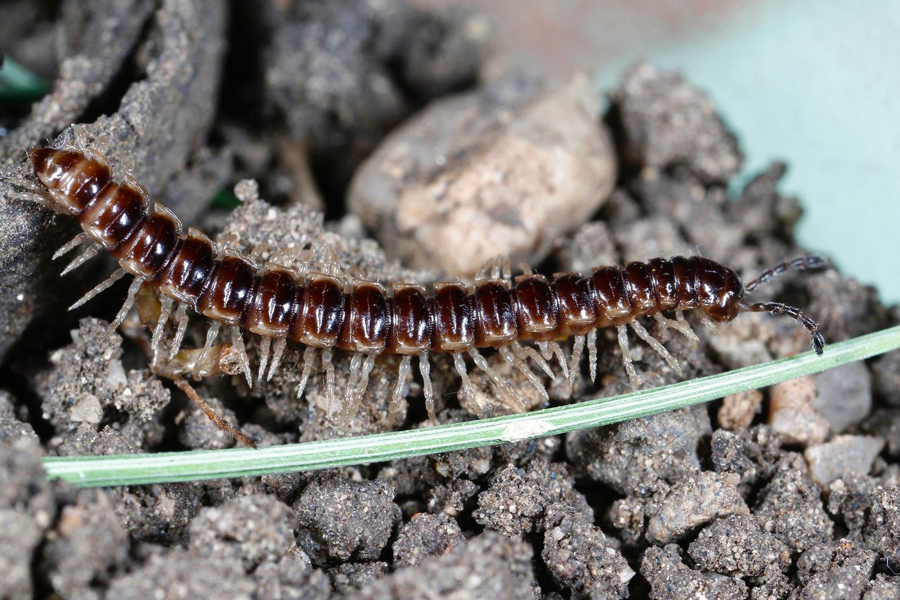

B 1088
Millipedes and Centipedes
This publication gives an overview of millipedes and centipedes and gives tips on how to control them in the home.
Elmer Gray
|
-
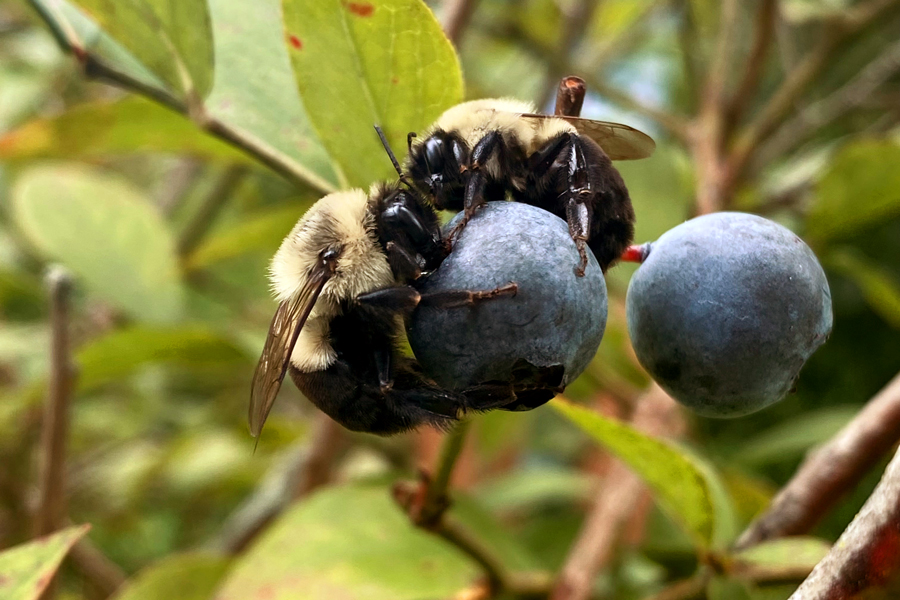

Esta guía muestra las abejas silvestres más comunes de las plantaciones de arándanos en el sur de Georgia. El material presentado aquí es un resumen visual del muestreo de 2021 y 2022 en campos comerciales de arándanos de los condados productores más importantes: Bacon, Pierce y Ware. En total, se encontraron más de 70 especies de abejas. La contribución de las abejas silvestres a la polinización de los arándanos es cada vez más reconocida. La identificación adecuada de estos insectos en el campo es una parte fundamental de los esfuerzos de conservación.
Sarah Miranda Rezende, Bodie V. Pennisi, Michael Ulyshen, and Jason Schmidt
|
-
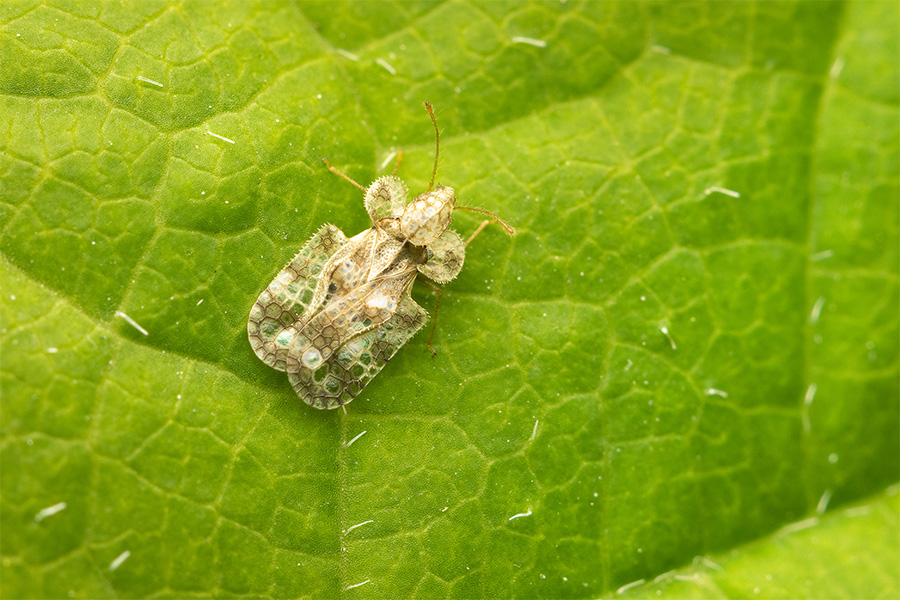

This resource covers lace bugs in landscapes, which can damage the foliage of trees and shrubs and detract from their beauty and, in severe cases, kill the plants.
S. Kris Braman
|
-
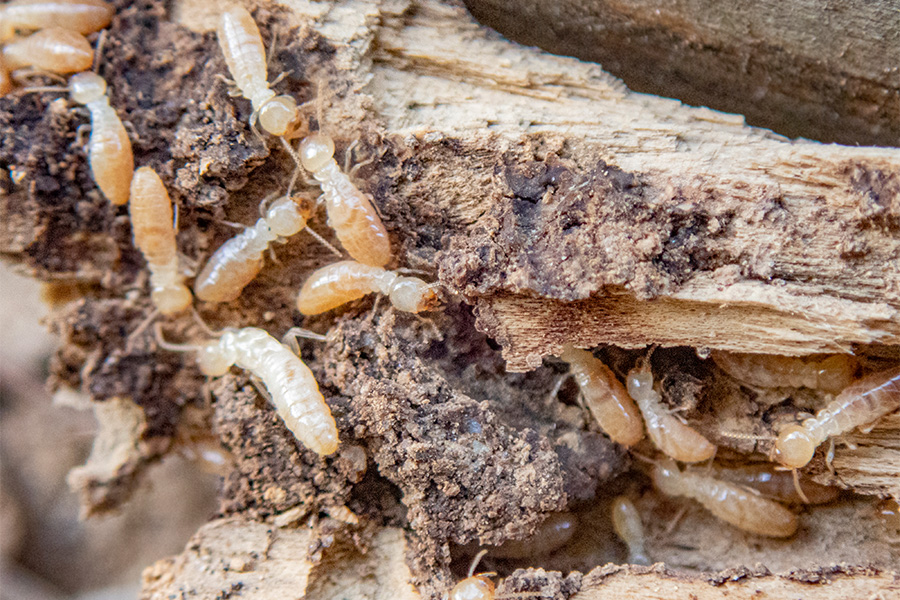

Las termitas subterráneas son los insectos sociales que viven en una sociedad en donde la mayoría de los miembros son insectos inmaduros o juveniles. Sus colonias pueden incluir de miles a millones de termitas, y a pesar de tener un cuerpo-suave, frágil y delicado son insectos formidables. En la naturaleza, las termitas subterráneas están estrechamente asociadas con el hábitat o entorno del suelo en donde construyen túneles para localizar agua y comida (ej. madera, troncos, y otras materiales que contienen celulosa).
[Subterranean termites are social insects that live in societies whose members are mostly mature individuals. Their colonies, which can contain thousands to millions of termites, are formidable, even though each individual termite is soft-bodied and delicate. This publication contains comprehensive information about subterranean termites in the Eastern U.S.]
Dan Suiter
|
-
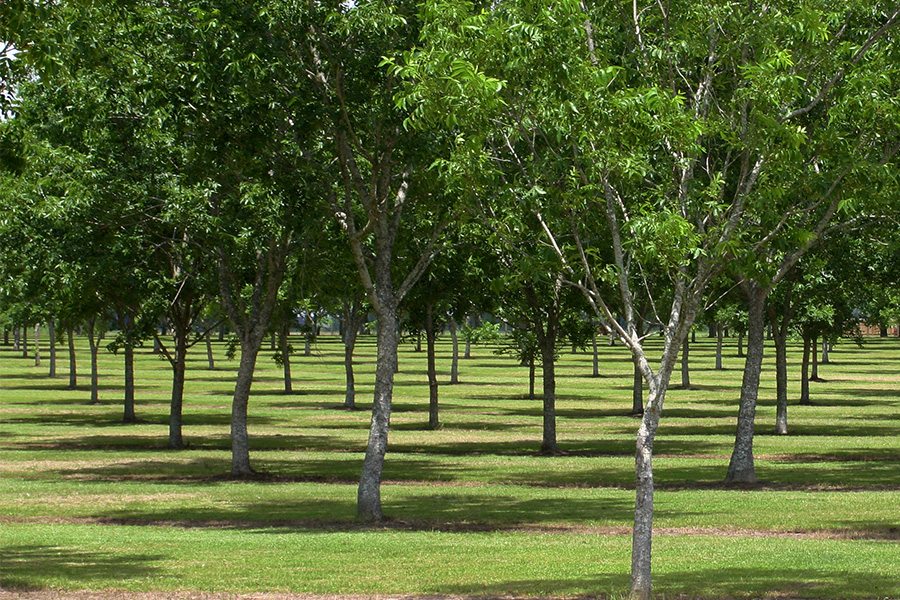

As Georgia’s pecan production acreage has increased, reports of insect pests that attack younger, less established trees have also increased, particularly infestations by pecan bud moth and ambrosia beetles. This circular summarizes the pertinent insect pests that attack young, non-bearing pecan trees, including key details on their biology, injury, monitoring, and management. This information should be helpful to both new pecan growers and experienced growers with newly established orchards.
Andrew Sawyer
|