Plant Pests and Diseases
-
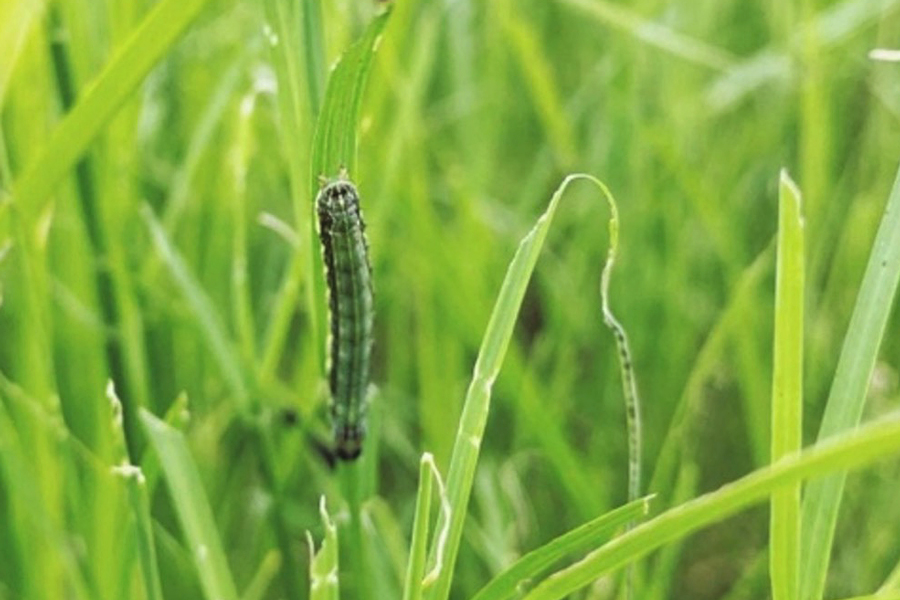

Fall armyworms can quickly decimate a field of any forage crop or pasture, often eating higher quality forage first. Growers and farmers can face severe economic damage and total forage loss. Anyone growing forage or pasture used to feed livestock can use this publication to find answers to the most common questions about fall armyworm in Georgia pastures and hayfields.
Savannah Tanner, Lisa Baxter, and Shanna Reynolds
|
-
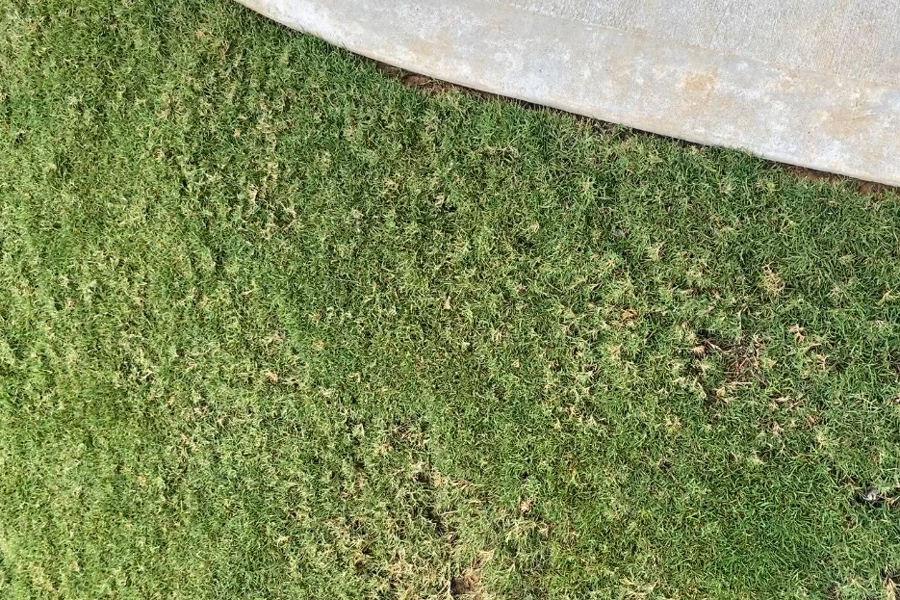

Bermudagrass mite is a microscopic mite species (at or smaller than ~0.2 mm or 0.0078 in.) that only infests and feeds on bermudagrass and has become an increasing problem in Georgia. It can develop into a serious problem on golf courses, athletic fields, sod farms, and both residential and public lawns. Bermudagrass mite infestations can reduce the aesthetic value of the turfgrass, causing thinning and poor grass growth. The size of bermudagrass mites poses a real challenge in identifying and monitoring the population in fields.
Shimat V. Joseph
|
-
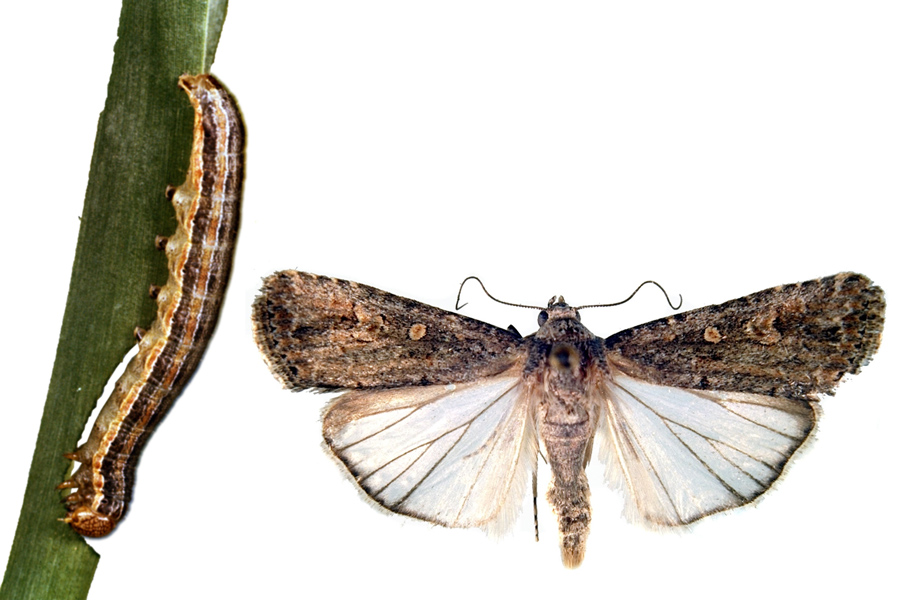

Fall armyworms are native to North America and can destroy lawn grass and other turf. They first reach Georgia in the spring or early summer, and caterpillars are noticeable in turfgrass in early July. The third, fourth, and fifth stages of fall armyworm caterpillars are the destructive stages. The younger stages (first through third larval stages) are tiny and hard to see in the grass. When infested, green turfgrass will gradually turn brown as the caterpillars grow. The damaged turfgrass may appear diseased or like it experienced drought.
William G. Hudson and Shimat V. Joseph
|
-
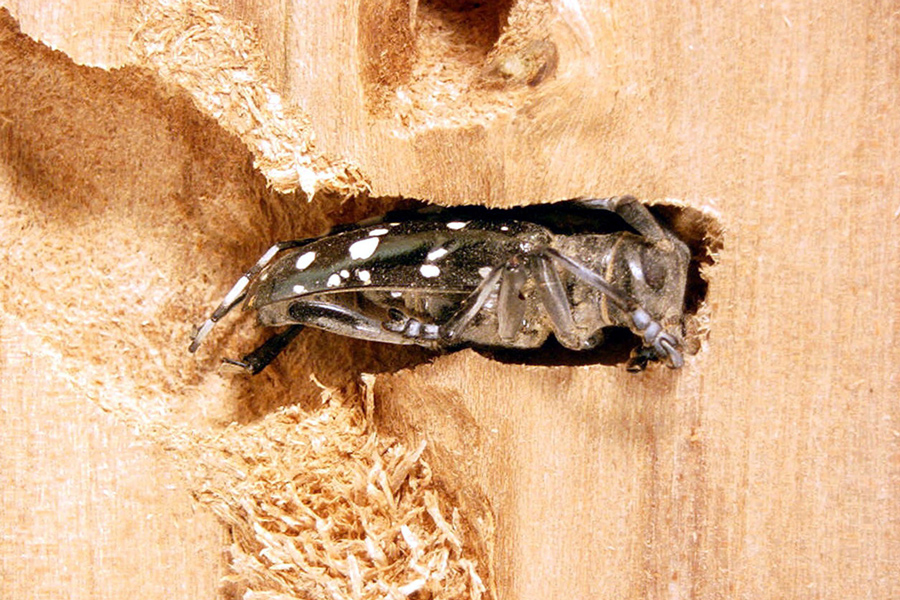

The Asian longhorned beetle is an invasive insect pest native to China and North and South Korea that threatens many hardwood trees in forests and landscapes in the United States. The pest is also referred to as the roundheaded borer because the segment below the head is round in shape.
William G. Hudson and Shimat V. Joseph
|
-
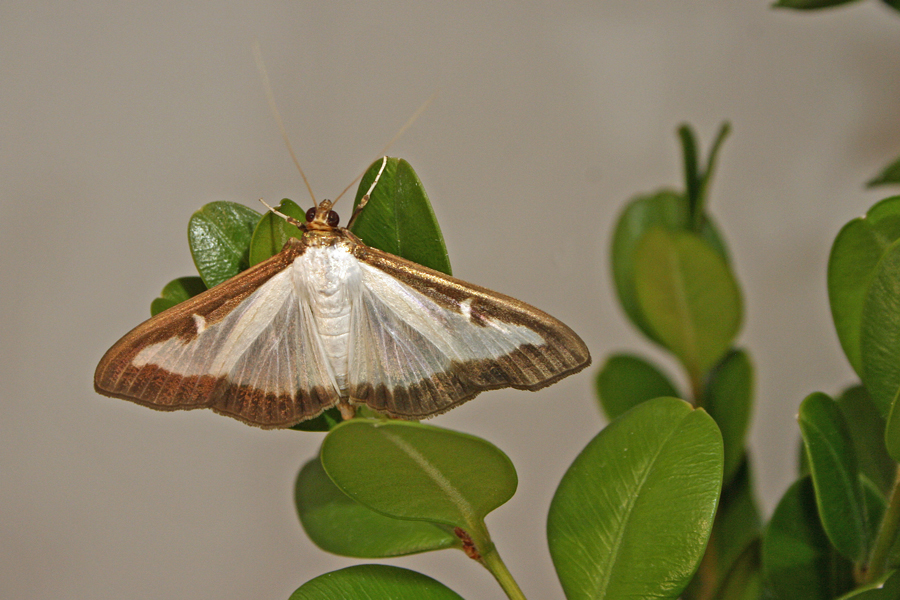

Box tree moth is an invasive pest of boxwood plants. It was introduced into New York in 2021 and has been reported in six other states. It has not been reported in Georgia yet. Boxwoods are an important ornamental evergreen shrub in the southeastern U.S., widely planted in residential, commercial, and public landscapes in both urban and suburban areas.
William G. Hudson and Shimat V. Joseph
|
-

The walnut caterpillar is native to North America and is mostly distributed in the eastern part of the United States. The larvae feed on the leaves of the plants such as pecan, walnut, butternut, and other species of hickory. Although it is an occasional insect pest, it feeds voraciously. This publication provides growers with information about its biology, damage symptoms, and management options.
William G. Hudson, Apurba Barman, and Rajendra Acharya
|
-
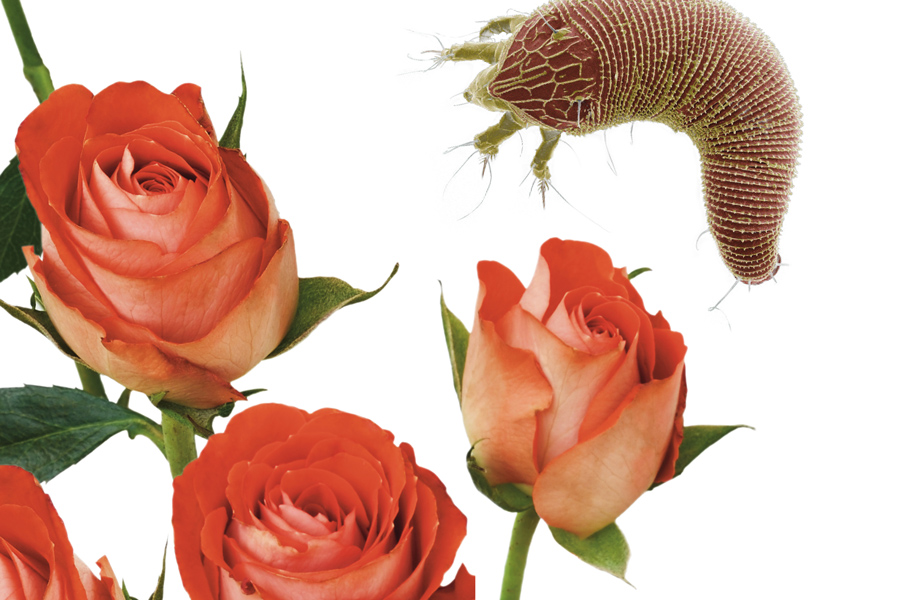

Rose rosette virus can cause major problems for nurseries, landscapers, and gardeners alike. The virus causes the plants to become undesirable and will eventually result in the death of the plant, which affects all segments of the rose industry as well as rosarians and home gardeners. The symptoms of disease on ornamental roses are a yellow mosaic pattern appearing on leaves, increased thorniness, abnormally shaped foliage and early production of lateral buds that make up the witches’ broom. This publication is intended for rose producers and serious rose gardeners interested in technical details of this virus and a mite that transmits it.
Jean Williams-Woodward, William G. Hudson, Bodie V. Pennisi, Shimat V. Joseph, and Alejandra Monterrosa
|
-
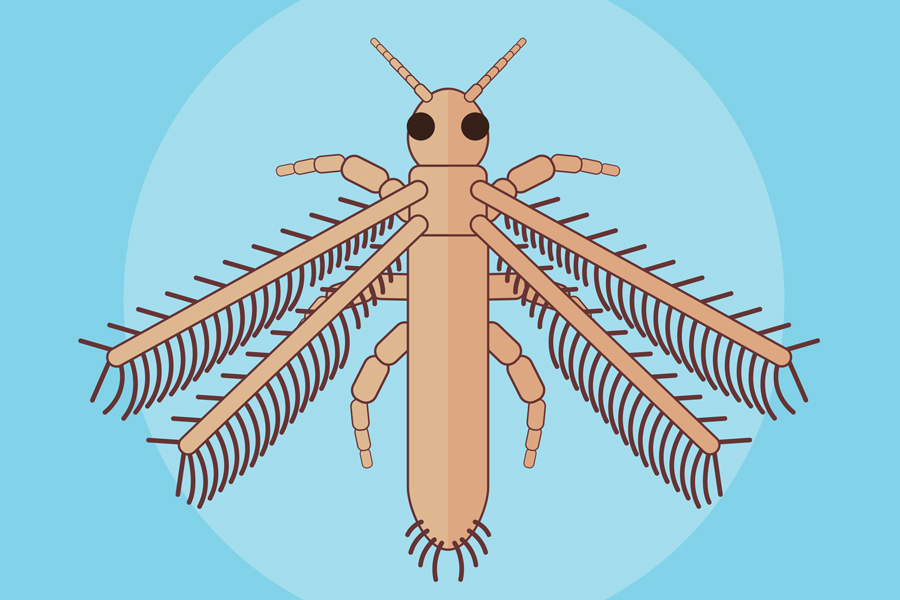
Thrips are tiny, cigar-shaped insects, with about 5000 known species, many of which cause damage to cultivated plants by feeding or spreading plant diseases. It is usually difficult to identify thrips species. Although they are winged, thrips are generally weak fliers, but they can be dispersed by wind and the transport of infested plant material. Some of the common thrips affecting landscape and nursery plants are described here.
William G. Hudson, S. Kris Braman, Shimat V. Joseph, and SHAKUNTHALA NAIR
|
-
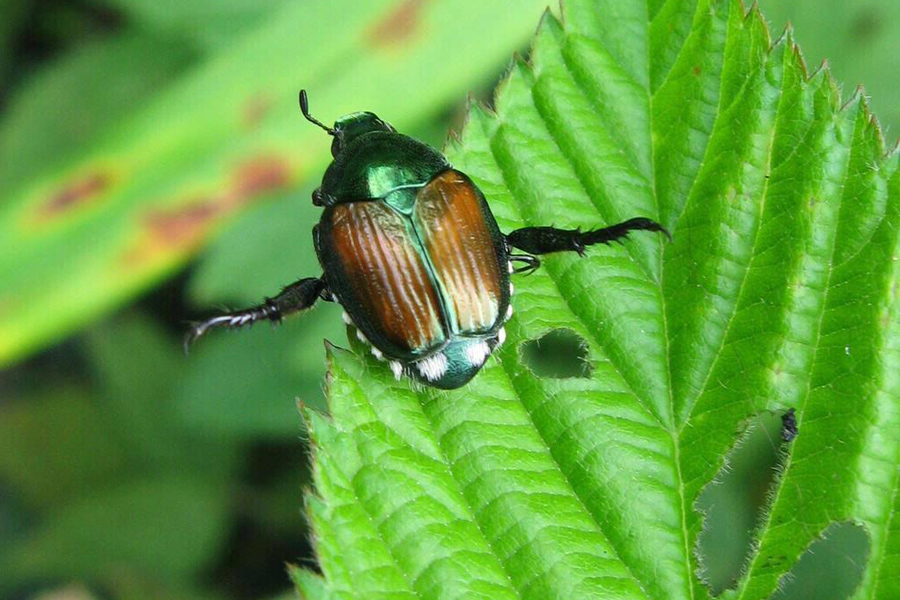

The Japanese beetle, as the name suggests, is native to Japan and was introduced to the U.S. through the transport of plant material. It is a highly devastating pest, attacking a variety of landscape and garden plants, fruit trees, field crops and turf. This circular provides an overview of Japanese beetles in the nursery and landscape, covering the biology, damage, monitoring, and management of this pest.
William G. Hudson, S. Kris Braman, Shimat V. Joseph, and SHAKUNTHALA NAIR
|